
"It is
impossible for ideas to compete in the marketplace if no forum for
� their presentation is provided or available." �������� �Thomas Mann, 1896
Network Security Manager
Contributed by Intellitactics, Inc.
�
Network Security Manager
is the holistic integrated threat management platform for Security Operations
Centers of Global 1000 companies, governmental organizations, and Managed
Security Service Providers (MSSPs) who need to deliver more effective
information security management at a lower cost.
NSM lets you police,
prioritize and prevail across today’s information security threats, so you
can understand security situations with unparalleled clarity in real time and
over time, and respond effectively in moments instead of days, with fewer
resources. NSM saves you time and money while protecting your information
assets and your organization’s integrity.
Unlike other security
products, the NSM platform integrates the enterprise through intelligent
correlation across all types of security devices and other information
sources, providing a graphical single-pane-of-glass visualization of threats,
anomalies and trends that are happening not only in real time, but over time,
so you can deliver enterprise-scale security management and response.
NSM has set the industry standard for security analysis. NSM’s holistic
approach, native intelligence, visual correlation and ability to seamlessly
integrate analyst investigations all work together to achieve one goal:
Helping analysts understand the threats, risks, scope and nature of the
security situation so that the appropriate response becomes apparent and the
security team can prevail in the relentless battle for enterprise security.
This white paper explains NSM’s capabilities and provides a high-level architectural overview, focusing on the correlation, scalability, visual security and response capabilities NSM offers.
General
Capabilities provided by NSM
Intellitactics NSM
gathers information in real time and via batches from all your security
devices and other information sources, correlates it, and provides real-time
security views, over-time reports, trend analyses, automated responses and a
powerful command-and-control console from which analysts can launch
interactive responses to emerging security situations.
NSM is a comprehensive
technology, offering many discrete capabilities within its architecture. On
their own, each of these capabilities provides tactical value to
organizations. Taken as a whole, the full strategic power of NSM begins to be
understood.
Log Consolidation
NSM makes the
perfect log consolidator: It supports all popular protocols, all manner of
back-ends (i.e. Oracle, SQL Server, Flat Files). NSM can be dropped in,
directly replacing existing syslog servers and other log consolidation
technologies. Web-based access to search and report on logs means NSM is the
demarcation point for audited and controlled access to all enterprise log
data.
Log Aggregation
NSM gives you
the option of aggregating logs to save on the amount of space used in the
back-end database. NSM allows aggregate data to be stored in databases, while
giving you the choice to maintain 100% of all flat file records for forensic
purity. NSM also has the ability to store 100% of all records, with no
aggregation, into relational databases and log management systems.
NSM supports
multiple parallel databases, for excellent data scalability (any JDBC database
can be used; Oracle and MS SQL are officially supported).
Data Routing
A data routing
rule defines where NSM stores historical event data. NSM provides flexible
data routing possibilities. It features a user-configurable ‘persistence
rule’ for defining how incoming data is routed. Data can be routed to flat
files, multiple databases in parallel (any JDBC database can be used, Oracle
and MS SQL are officially supported), SNMP traps and additional NSM software
in your environment. NSM allows you to route data based according to specific
attributes, including priority, business unit, customer, type of data and
level of suspicion, all through a simple visual rule editor.
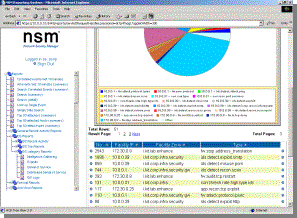
Reporting
NSM’s web
reports offer both high level and detailed views of historical security data.
NSM ships with a significant number of reports designed to provide valuable
information to all levels of the organization, including SOC analysts,
managers, and corporate executives.
NSM’s reporting engine is not based on “third party” reporting plug-ins,
and is heavily optimized to expand on the industry standard paradigm of
“drill down” by introducing a concept we call “hyper-drilling.”
Hyper-drilling allows one-click browsing in many dimensions, and makes it
easier for analysts to follow the path of an attack. Hyper-drilling actually
“correlates” the possible hyper-drills and allows for
“chain-of-evidence” browsing.
e.g. START: Show all attacks in DMZs
-
Zoom in on an attacker
-
See what types of attacks this attacker initiated
-
For a particular attack type, find out which asset was targeted
-
For a particular target, see if it was compromised and then targeted other hosts
-
Drill down via ports, mac addresses, signature names, business units, etc.
Real Time Correlation
NSM performs
correlation in memory at very high speeds, and maintains correlation-engine
state in an object store wherever NSM is installed. This object store
maintains an object-oriented data model of security relationships and is
specifically designed to allow NSM’s correlation algorithms to run at high
speeds.
The correlation engine cross-correlates data from various sources, including routers, firewalls, IDSs, HTTP Proxies, DHCP servers and OS Logs, enabling analysts to detect threats such as subtle “low and slow” attacks, NIMDA-like hybrid attacks based on traffic flow analysis, DDOS detection, needle-in-the-haystack rare event detection and more.
Intellitactics’ correlation engine provides the unique ability to correlate user activity out of the box. Users are often the source of internal attacks, and NSM’s correlation engine analyzes user activity separately from network activity.
Intellitactics scores correlated events based on the sophistication of the attack, the importance of the assets to business continuity, the sensitivity of information and knowledge about the asset (including vulnerability data).
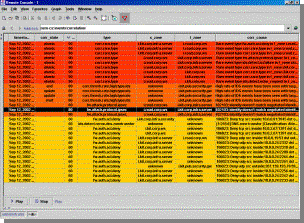
Historical Replay (re-correlation)
NSM supports the replay and re-correlation of historical data. Data stored in flat files, as well as data in the database can be replayed back into NSM. NSM gives users the capability to replay information retrieved in a report. For example, an analyst can query user activity for the past two months, and replay the results into NSM to re-create correlated conclusions and visualizations of the user’s potentially damaging activity.
�������
 ��
�� 
������� Query��������������������������������������������������������������������� Results
������
 ��
�� 
Re-Correlated
NSM permits replay of historical data, even while it is processing real-time data. NSM has the intelligence to keep the two data feeds separate. This ensures that both data feeds aren’t compromised or distorted.
Security Threat Visualization of Hybrid and Subtle/Complex Attacks
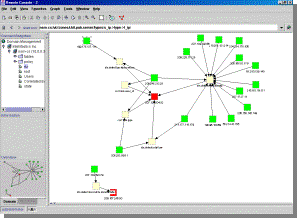
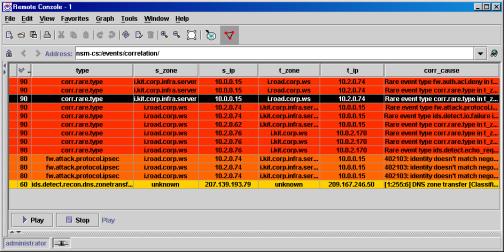
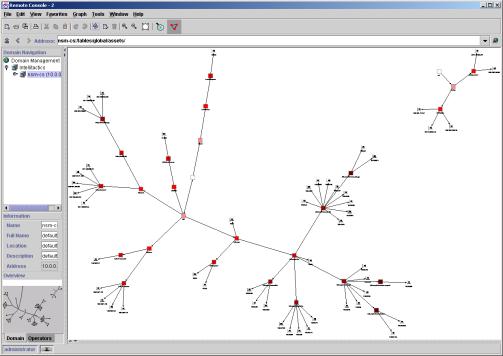
NSM excels at displaying large volumes of events visually, in innovative ways to highlight the strategy and nature of the attack. Hybrid attacks, which can not be detected by a single point solution, are clearly identified in these views. Multiple, unrelated situations are also easy to spot. NSM is one of the few systems that can identify if two or more unrelated security situations are occurring simultaneously. Historical views are represented as 2D topological maps with dynamic color coding to identify suspicious hosts, dangerous activity and in-progress attacks vs. historical patterns.
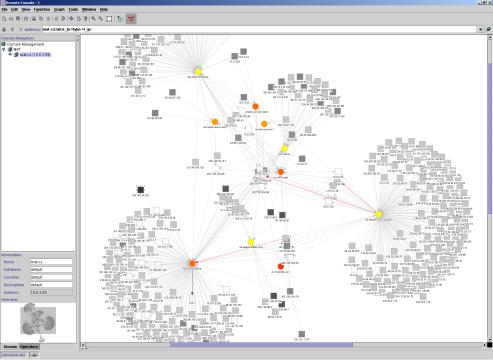
Colors
represent groups of events. Suspicious IP addresses go from�
pale to dark as they become more
suspicious�������� (e.g. Black Hat).
Trend Analysis
Next-generation security trend analysis can be performed with NSM Advanced Analytics™.
Intrusion Prevention (Automated Response)
Users can configure NSM to launch automatic responses when criteria specified by the customer are met. Automatic responses can be, but are not limited to:
-
Automatic creation of a trouble ticket
-
Disabling a user account
-
Shutting down a service
-
Shutting down a machine
-
Blocking an IP address
-
Resetting TCP/IP communications
-
Launching automated vulnerability scans of attacked hosts, or attackers
-
Starting sniffers automatically to record network traffic as it happens with very little delay
It is
important to note that just as NSM architecturally abstracts all
products/devices sending events into one common framework, NSM also
architecturally abstracts response. Not all firewalls allow blocking of an IP
as a response option. The response capabilities depend on the capabilities
your infrastructure possesses. NSM links to your existing infrastructure, and
depends on the capability to implement a response. For example, shutting down
a service or machine requires that NSM have access to that service/machine,
with all appropriate rights and privileges, to be able to achieve the
response.
Correlated Response
In NSM, every
event and object is “alive”, and right-clicking on an event causes NSM to
correlate the actions associated with the object. Clicking on an attacker
presents different options (i.e. block IP) vs. clicking on a user object (i.e.
disable user account). In this way, NSM provides a rule-driven, audited,
command and control GUI from which actual response may be driven.
Integration with MOM Technologies
NSM’s ability to correlate complex security situations and present them in easily understood descriptions allows for successful interfacing to Manager of Manager technologies, such as HP Openview, IBM Tivoli and CA Unicenter. Successful integration with MOM technologies is dependent upon meeting two main requirements: 1) avoiding flooding the MOM (correlation is key here), and 2) ensuring the events sent to the MOM are clear, understandable and actionable by non-security staff. NSM achieves this by describing both the probable cause of the security situation, and a suggested response.
Main Components of the NSM Architecture
Intellitactics NSM is an
enterprise software application that supports a variety of platforms. The main
components of the NSM architecture include:
Central Server (CS)
The main engine of the NSM architecture. Contains license management, access control database and cross-NSM correlation capabilities. Receives events from many protocols: Syslog, SNMP, SMTP, TCP/IP, OPSEC and NSM Event Consolidators. Normalizes, filters, correlates and takes any responses set by policy. Typical deployments include one Central Server per Security Operations Center.
Event Consolidator (EC)
The key to
NSM’s enterprise scalability. Receives events from many protocols: Syslog,
SNMP, SMTP, TCP/IP and OPSEC. Normalizes, filters, correlates and takes any
responses set by policy. Sends correlated events to NSM Central Server for
cross-NSM correlation. Initial deployments typically include one to three ECs,
depending on event load and number of geographic locations. Additional ECs are
added as NSM is scaled to meet a growing enterprise role.
Remote Console (RC)
The Remote Console, the GUI part of the application, enables users to log in (they are authenticated against a Central Server) and begin monitoring security in real time, based on the view of choice. NSM offers several ways to monitor/view activity:
-
Correlated event views that display the most significant threats by exposing the type of threat, the location of the threat and how it will impact your business
-
Visual Security™ �- graphical visualizations that display thousands of events visually to show interrelationships that would otherwise be hidden, such as Denial of Service attacks and low and slow hacker attempts �
If users have
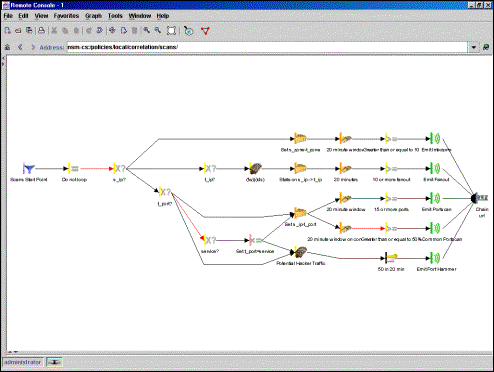
been granted suitable permissions, they may also edit specific policies and
develop new correlation rules, using the Remote Console.
The Remote
Console gives analysts the ability to copy/paste policies across Event
Consolidators distributed across the organization.
All Remote
Console communication to other NSMs is encrypted via SSL provided by Java
Secure Sockets library.
Advanced Analytics
NSM Advanced
Analytics™ enables you to accelerate your investigation of threats, quickly
conduct in-depth analysis to support forensic investigations and make
effective strategic and tactical decisions to improve your organizational
security and anticipate future threats.
Advanced Analytics is a powerful forensic tool that provides a multi-dimensional view of massive amounts of log data extracted from log repositories (databases and flat files). Advanced Analytics exposes hidden security threats, transforms disparate data into actionable graphical information and visually tracks security situations over time. Because Advanced Analytics presents historical data in patterns and trends, organizations can unmask threats disguised by mountains of event data, which would be virtually impossible to identify through any other method.
Installing NSM
Intellitactics has made
NSM easy to install. NSM ships on one CDROM, and offers a multi-platform
InstallShield. The application typically takes 15-20 minutes to install and
occupies fewer than 200MB. The only hard requirement for installation is a
license key, which identifies the local system on which NSM is installed. The
location of the primary database (if applicable) can also be specified at
install time.�
During the installation,
the user is presented with options to install Central Servers, Event
Consolidators, Remote Consoles and the Reporting System.
The configuration of NSM is stored primarily in two files. One is a property file, which contains license and related data. The other is a local object-store. This local object-store contains all the policies, configuration data and correlation state. When backing up NSM, the only file you need to ensure you back up is the local object-store. This makes NSM’s configuration easy to manage operationally. Further, NSM is stored primarily in one directory for easy management.
NSM offers role-based access for increased security. Access control occurs through a central authentication framework. Access controls exist for application and data. The NSM administrator can assign rights and privileges as far down as graph level and can allow multiple users to access to the same server.
Deciding what to aim at NSM
The power of NSM becomes
apparent once you connect it to information sources (firewalls, IDSs,
operating system logs). As NSM supports a great many products (over 100),
across many operating systems and architectures, you can well imagine there
are many options and ways of sending information to NSM. To make the job
easier, Intellitactics has adhered to three primary goals: to minimize effort
in adding devices, minimize agent dependency, and minimize the number of
software installs required.
Organizations often
debate which device types to aim at NSM. The table below covers a relative
value scale on how insightful Intellitactics has found the information from
specific devices (i.e. how likely a particular source of information will be
in helping you zone in on a real attacker in today’s real-world
environments). The list below should not be interpreted as how useful the
devices are as part of a security infrastructure, only how useful their
logs/event data are in successfully finding significant security breaches.
Technology Type���������������� Point Value (relative usefulness of data)
Web Proxy Servers����������������������������� 35
Host based IDS���������������������������������� 25
Any ‘netflow’ type data������������������������ 25
Network based IDS����������������������������� 20
Router����������������������������������������������� 15
NT Logs��������������������������������������������� 15
UNIX Logs������������������������������������������ 15
Firewall���������������������������������������������� 10
VPN�������������������������������������������������� 10
Any sniffer type data��������������������������� 10
Anti Virus�������������������������������������������� 5
PKI Log����������������������������������������������� 5
Information flow in NSM
One of the keys to NSM’s scalability is its inherent separation of “real-time correlation” and “long-term storage” of event data (for reports and historical analysis). The optimal solutions to these problems require separate approaches. Many event management solutions have scalability issues as their real-time correlation engines largely depend upon a repository. If this repository is ever down, the usefulness of the entire system is compromised. This does not occur in NSM. The diagram below shows the information flow for a single Event Consolidator (EC):
�
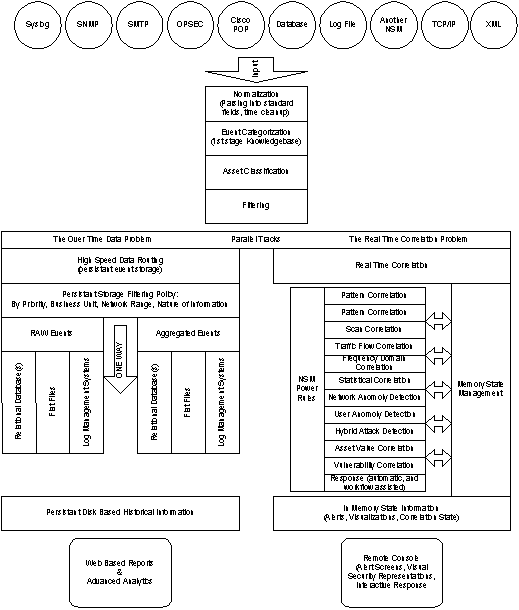
Various processes are engaged as information flows through NSM:
Normalization
Normalization
is the process of breaking data into standard fields. Standard fields include
source and target IPs.
Categorization
NSM considers many factors in establishing categories and priorities for events.
What taxonomy
category does the signature belong to? (i.e. a DOS attack is initially higher
than a RECON attack.)
Signature Knowledgebase
More than 5
years ago, Intellitactics started building what is now the largest security
knowledgebase in the world. Approximately 60,000 signatures are modeled in NSM
across many product areas (FW, IDS, AV, OS, PKI, etc.) and mapped into a
hierarchal categorization system known as the Intellitaxonomy™. NSM’s
security knowledgebase is the largest in the industry by at least a factor of
4 in breadth, and incalculably more useful in depth.
The Intellitaxonomy knowledgebase serves two purposes:
-
To demystify security events by explaining probable causes and suggested responses in clear, easily understood messages. For example, it doesn’t matter what kind of IDS is operating in your environment (Snort, ISS, Dragon, Sourcefire, NFR, etc.). NSM reports the security interpretation of those events consistently across products.
-
Enhancing the power of the NSM event correlation engine.
�
The
knowledgebase is organized into several major areas, each representing
specific cross-product knowledge. These value-added categories consolidate
similar messages into meaningful common security type threats. For example,
ids.detect.dos encompasses the family of all DOS attacks, including
distributed denial of service attacks. In essence, NSM offers additional
security subject matter expertise gathered over years of experience, making
the security team more effective in less time. Knowledgebase categories
include:
Defense / Infrastructure Analysis
NSM relies on the following types of information to gage the strength of defense capabilities in a specific environment:
-
Vulnerabilities
-
Virus Scans
-
Insecure Communications
-
Directory and PKI
-
Crypto
User Analysis
NSM actively models the concept of a “user,” and builds a model to identify suspicious user activity by monitoring the types of information users access and how they interact with information sources.
-
Configuration Changes
-
Remote Access
-
File / Object Changes
-
Authentication / Authorization
-
Application Use
Anomaly Detection
Many types of events NSM correlates do not individually signify an attack. However, when correlated together using anomaly detection algorithms, these combinations of events can expose next-generation hybrid attacks. Attacks like the “Slammer” are detected and classified using NSM’s anomaly detection capabilities.
-
Protocol Behavior
-
Reconnaissance
-
Process Tracking
-
Corrupt Information
-
Compromised Hosts
-
Traffic Flows
Intent Classification
There is a difference between a “robotic” or “automated” attack, and a stealthy employee trying to access systems. A section of the Intellitaxonomy knowledgebase informs users and NSM’s correlation engine so that the strategy of attacks can be clearly seen.
-
Attack Strategy Classification
-
Backdoor
-
DOS / DDOS Attacks
-
Exploits
-
Worms
-
Trojans
NSM’s hierarchal organization of security events lets users report on or visualize entire “groups” of related events. For example, ids.detect.dos encompasses the family of all DOS attacks, including distributed denial of service attacks, while auth.login.deny contains all denied logins, including VPN, Radius, Active Directory, application, etc.
If you were interested in identifying the types of misuse occurring in your network, a report by business unit, user or workstation for “ids.detect.misuse,” would match the following categories of misuse:
��������� ids.detect.misuse.game
��������� ids.detect.misuse.chat
��������� ids.detect.misuse.spam
��������� ids.detect.misuse.warez
��������� ids.detect.misuse.peertopeer
��������� ids.detect.misuse.gambling
��������� ids.detect.misuse.filesharing
��������� ids.detect.misuse.pornography
��������� ids.detect.misuse.jobs
���������
ids.detect.misuse.stocks
NSM clearly
distinguishes the types of misuse occurring, so you can respond effectively.�
Example Intellitaxonomy Categories
Each
Intellitaxonomy category contains not only a category descriptor, but also
probable cause descriptions, as well as suggested responses. This information
makes the job of a security analyst easier, as it clearly explains the problem
and recommends appropriate solutions.
Category: ids.detect.exploit.nfs
Description: An event of this type is generated when a source attempts to exploit a vulnerability (bug) in an NFS client or server. There is no indication that the exploit was successful. NFS (network file system) is a protocol which allows file systems to be exported and mounted remotely. It is similar in concept to Windows File Sharing. Historically, it has not supported strong access control and has had many vulnerabilities, but that has since been improved.
Recommended
Response: You should consider the source to be hostile and check to
see what other events it may have been involved in. Determine the zone
orientation of the event by looking at the source and target zones. If the
source is internal, investigate the event as a possible internal compromise
(why would one of your own machines be sending an exploit?). If the source is
external, verify that your internal hosts are properly protected. Check to see
if you are actually running the target service or client. You may also inform
the source's administrator as the source may itself be a compromised machine.
Determine the client/server orientation by looking at the port numbers.
Category:
ids.detect.dos
Description:
An event of this type is generated when a group of sources performs a
denial of service attack or traffic is seen from a single source that appears
to be characteristic of traffic generated during a distributed denial of
service attack. These attacks are usually attempts to consume all available
bandwidth and processing power available to a site. The target IP may not
actually be the target of the attack if the attack is of the "smurf"
type and the target is a network broadcast address; in this case, the source
IP will be the target of the attack.
Recommended
Response: You should consider all IP addresses involved to be at
high risk. Check your current bandwidth utilization and check for other recent
DDoS activity. Try to determine your position in this attack. Are you the
target, the source (with compromised machines acting as DDoS agents), a relay
(in a smurf attack), etc? If you find that you have compromised machines with
participating DDoS agents, try to gather information about the controller of
the agent (via packet captures, IDS signatures, etc) so that the real source
of the attack may be identified. If you are the target of a DDoS attack,
contact your upstream providers immediately and attempt to block the offending
traffic as far upstream as possible.
Category: ids.detect.dos.msdtc
Description: An event of this type is generated when a source runs a denial of service attack against the MSDTC service (providing distributed transaction functionality for services such as MSSQL and IIS). These attacks are usually attempts to exploit bugs in the service with the hope that the service will crash as a result.
Recommended
Response: You should consider the source to be hostile and see if
it has generated any activity in the past. Also, check to see if you are
actually running an MSDTC service on the target host (MSDTC is associated with
IIS and SQL Server). Check to see if MSDTC is still available.
Asset Classification
NSM helps you
prioritize and focus your response through asset classification. NSM spells
out exactly where the trouble is (for instance, marketing.ny, or webfarm.dc)
so you instantly know where in your business the asset is located and what
business processes it manages. NSM allows easy asset classification of
business units, functions, critical servers, etc. based on a priority ranking
scale from 1 to 100. By classifying assets in NSM, you instantly know the
business value of the assets involved in a given security situation as it is
unfolding, helping you prioritize and decide on action. You can also include
contact information to assets to accelerate response. NSM combines the
Intellitaxonomy knowledge base, intelligent correlation and asset
classification to pinpoint the business assets affected, their business
priority, and the potential impact on critical business processes.
Assets can be bulk imported from existing systems (e.g. HP Openview or a Directory).
Real Time Correlation
NSM provides significant correlation capability out of the box through preloaded PowerRules™. A real-time, multi-threaded correlation engine considers each event received by NSM and examines it against a set of decision criteria, such as:
-
Is this a rare or unusual event?
-
Is this a repeat attack from a known attacker?
-
Does the target have a known open port that is being targeted?
-
Does the target have a known vulnerability?
-
Is the target mission critical, or contain sensitive information?
-
Is this event part of a larger scan or strategy?��������������
NSM’s general approach to correlation involves to running dozens of different types of correlation algorithms and approaches in parallel to maximize the amount of conclusions that can be reached about the data.
A tour of the
types of correlation NSM provides out of the box:
Heuristic Correlation
Starting with
NSM 4.0, heuristic correlation of free-form syslogs is performed for Solaris
servers. This type of correlation reads keywords and analyzes combinations of
important terms to determine the probable actionable content of the message
(i.e. the term “kernel and error” in a syslog is more likely to be a
kernel error than an NFS issue).
IDS Correlation
Classification
of DOS, DDoS, Recon, Misuse, Backdoors, insecure protocols, VPN attacks,
configuration changes and much more. NSM understands HIDS and NIDS.
Firewall Correlation
Classification
of normal activity, errors (fail over, VPN, memory limit issues, etc.),
configuration changes.
PKI Correlation
Certificate
issuing, revocation, configuration changes, etc.
OS Modeling
Logins,
Logouts, User/Group creation / deletion / updates, account policy updates,
restarts, service changes, etc.
Configuration Correlation
NSM correlates configuration changes separately across devices by network, asset group or business group to determine configuration changes which should be noted.
Database Correlation
NSM correlates
database audit table events from databases such as Oracle. All schema changes,
inserts/updates/deletes, etc. are tracked and correlated.
Anti Virus Correlation
NSM correlates
data it receives from anti-virus messages as part of its overall correlation
system. NSM will tell you of rare and interesting viruses not seen before, as
well as viruses that couldn’t be cleaned by the AV engine that pose risk to
other users.
Email Correlation
You can
configure your mail servers to send a copy of all emails to NSM. NSM supports
keyword filtering, and visualization of from/to/subject patterns to rapidly
detect new and unknown email viruses.
Asset Correlation
NSM’s asset
management capability allows users to import large asset lists in the form of
IP addresses and network ranges. To these objects, NSM associates sensitivity,
criticality, function, and more.
Vulnerability Correlation
NSM can
receive information from vulnerability scanners (e.g. Nessus and ISS). NSM
augments its asset knowledge with vulnerability state information to further
reduce false positives. Vulnerability information takes the form of port
open/close knowledge, as well as specific found vulnerabilities from a scanner
(e.g. a CVE ID).
Comprehensive Scan Detection
-
Low and Slow Port Scans
-
Low and Slow Network Scans
-
Low and Slow Inter-Business Unit Scans
-
Common Service Network Scans
All NSM scan
detection is cross-sensor.
Port-Based Attack Strategy Detection
Attackers can
launch many methods against a specific service (i.e. web on port 80) hoping
that one of their methods will work and they will compromise the server. This
is not a classic port-scan, or network scan. It's an attacker trying to
penetrate a specific service. NSM correlates these activities into one clear
message, even if the attacker is clever, and uses several source IPs from
which to launch attacks.
Inter-Business Unit Scans
A workstation
that communicates with multiple business units in a time window.
Rare and Unusual Event Detection
By business unit and sensor
Rare User Activity
NSM will
detect new users it has not seen before, as well as users it has not seen in a
specified period of time (i.e. 30 days).
Burst/DOS/Anomaly attack detection for
-
Accepted Logins
-
Denied Logins
-
Firewall Traffic (accept/deny)
-
Configuration Changes
-
IDS Signatures per business unit
-
General DOS attacks (catch all)
Hybrid Attack Detection
NSM
automatically detects if the same source IP or user initiates recon, followed
by a DOS or similar attack. NSM even identifies non-traditional subtle
combinations of activity and informs you of the suspiciousness of the attack.
Target Modeling
NSM keeps
state on the “targets” of traffic. If multiple sources are used (to
disguise source of attack), NSM correctly identifies that a “coordinated”
attack is occurring on the target.
Visual Security
Visualizations of security situations by business unit
Visual
Auto-discovery of services run by servers
Auto Discovery of Services
With more
servers running “personal firewalls” or other port-blocking technologies,
it is more difficult for security professionals to be sure of which computers
are acting like servers. NSM will inductively build maps of which services are
running on your servers, group your network sensors, etc. together in views
dynamically. Often an eye-opener, this correlation lets you discover what you
are “really” running.
Auto Discovery of User Behavior Patterns
Most ESM
solutions perform mainly “signature” and “IP” analysis. Intellitactics
NSM goes beyond this with “out-of-the-box” discovery of user behavior
patterns. Feed NSM NT Logs, Web Proxy Logs, authenticated firewall logs, etc.
and see exactly what your users are doing visually.
Organizational Data Flow Discovery
“Why is a
marketing workstation talking to our accounting server?” and other
fascinating questions.
Unusual Configuration Times
Flag all
configurations done outside of a change control window as potentially
suspicious.
Correlating with Vulnerability Data
NSM can import
vulnerability scans from ISS, Nessus, and other vulnerability scanners. This
information can be used to further reduce false positives. In the case of the
same attack being launched against two hosts, one with a known vulnerability,
NSM will score the priority of the attack against the vulnerable host higher.
Web Proxy Correlation
NSM provides
deep correlation of web proxy logs. These logs contain much security value.
NSM helps analysts find users who are tunneling through proxies (establishing
2 way TCP/IP communications that bypass firewall policies), users whose
workstations are infected with spyware, bandwidth abuse, peer-to-peer file
sharing, other employee misuse. NSM produces reports and visualizations of
user activity so organizations can enforce their policies.
Big Board Visualization
Large
organizations often benefit from a high level visualization of corporate
security. NSM maintains a correlated view of business units and the types of
security events occurring within them. These views make it easy to spot
problems occurring in business units and also rapidly assess the scope of
problems occurring across business units. Many organizations choose to display
this type of view on a large plasma screen in a SOC, although this view is
also available from all remote consoles.
Intrusion Prevention / Automated Response
-
Automatic creation of a trouble ticket
-
Disabling a user account
-
Shutting down a service
-
Shutting down a machine
-
Blocking an IP address
-
Resetting TCP/IP communications
-
Launching Vulnerability Scans of attacked hosts, or attackers
-
Starting sniffers automatically to record network traffic
Additionally,
the rules in NSM allow definition of:
-
Flexible Notification
-
Email & Pager Notification
Intellitactics can configure NSM to notify staff based upon time, asset and condition.
-
If the SMTP server is attacked, then notify the email staff.
-
If the SMTP server is attacked after hours, notify additional staff.
Security Service Level Agreements / Assurance Groups
Specific groups of servers (i.e. all email servers, or a group of servers belonging to a project) can be grouped so specific reports can be created:
-
DOS attacks on Mail Servers
-
Configuration Changes on Routers / Mail Servers, etc.
Monitoring Executive Activity
If a list of executive account names is known, or a list of the IP addresses of their workstations is known, it is possible to have NSM produce a report of activity to their accounts and workstations. Executives often appreciate these reports because they can be assured that they are indeed the only ones logging in to their own accounts.
Customized Reporting
NSM's
reporting system is open, and can report on database tables other than NSM's
own event tables. Even publishing simple tables (i.e. a phone book table) can
provide considerable value, as web enabling them in NSM is straightforward.
New reports are defined via XML.
Scaling
NSM
Scaling NSM involves
the following steps:
1.������� Deciding where your SOC or headquarters will be
2.������� Deciding on the balance of local storage vs. distributed storage
3.������� Calculating how many Event Consolidators you need
4.������� Deciding how to geographically deploy ECs to save bandwidth (hierarchal deployments)
You can do load sharing
across multiple boxes compatible with third party load sharing
systems. However, NSM is extremely scalable in its design and it is
recommended to simply divide the load across multiple EC’s. In addition, NSM
supports the use of multiple databases. For example, all of the data can be
placed in a single database, then send the firewalls’ admin data to another
database and then again separate NT logs into a 3rd database.
A typical deployment of
NSM, consisting of 1 central server and 2 event consolidators, can handle
bursts of up to 5,000 events per second (EPS). Sustained throughput varies
from 3,000 EPS to 1,200 EPS depending on the correlation capabilities the
customer enables. Scalability of NSM grows linearly by adding more event
consolidators.
It is highly recommended
that in order to provide more accurate performance and throughput statistics,
Intellitactics calculates recommended configuration based on the customer’s
environment and desired requirements.
Failover and Redundancy
Intellitactics has a partnership with Stonesoft Corporation that enables Intellitactics to form failover clusters. In addition, NSM does not have a single point of failure as each event consolidator can have its own database.
NSM
GUI Overview
The Remote Console
The NSM Remote
Console monitors real-time security events and launches investigations and
incident response. The Remote Console is a Java application, and can be
installed on a central network share. This makes it easy to access and upgrade
Remote Consoles.
Remote Console GUI
Event Views
Visual Security
Visual Rule Editor
Web Access - NSM offers secure web access to hundreds of reports.
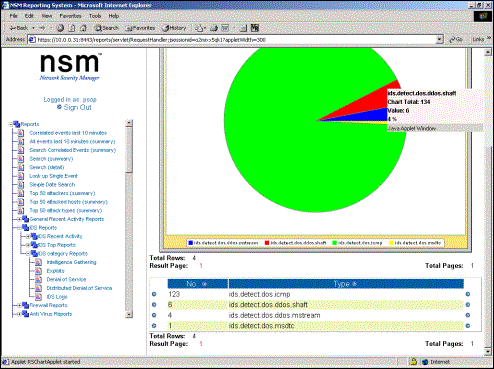
�
NSM Minimum System Requirements:
Windows/x86 platform
Operating System: Windows NT 4.0 Server with Service Pack 6a
Processor: Pentium III 733
Memory: 1024MB RAM (for
NSM CS, NSM RSS, and DB on same system)
768 MB (for NSM CS and NSM RSS on same system)
Hard Drive: Minimum 200 MB of hard drive space available for NSM system
Display Driver capable of 65K colors at 1024x768
Unix Solaris platform
Operating System: Solaris 8 with Solaris Common Desktop Environment (CDE)
Processor: Sun Ultra 10 Model 440 1x440MHz UltraSPARC-lli
Memory: 768 MB (NSM CS, NSM RSS and no database)
Display Driver capable of 65K colors at 1024x768
Advanced
Analytics
NSM Advanced Analytics™
is an add-on module to Intellitactics Network Security Manager that
dramatically expands the analytical power of your NSM™ holistic integrated
threat management platform. Designed for advanced users such as security
analysts, Advanced Analytics allows you to make effective tactical or
strategic decisions about your organizational security in a shorter period of
time.
While NSM correlates data in real time and near real time, Advanced Analytics is the only security tool specifically designed to give you a progressive, in-depth view of your security infrastructure over longer intervals.
NSM Advanced Analytics:
-
uncovers hidden security threats
-
transforms disparate data into actionable graphical information
-
visually tracks security situations over time
-
presents historical data in patterns and trends.
As it tracks hundreds of
thousands of events, Advanced Analytics reveals patterns and trends, including
unusual levels of communication between workstations and servers, spikes in
errors on your Web server and abnormally low levels of activity on security
devices, cluing you in to irregular behavior so you can proactively identify
potential threats and take action immediately.
Advanced Analytics can
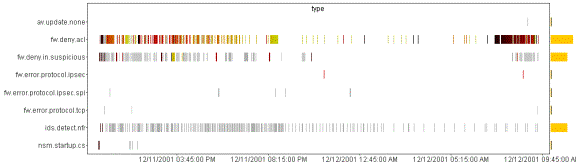
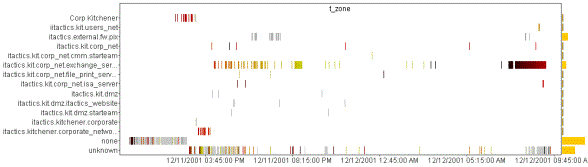
be completely customized based on the user’s preferred view. The example
above shows several different types of views available for trend and forensics
analysis. The data populated into Advanced Analytics comes straight from NSM.
�
In the first pane, you
can see both correlated and/or raw events.�
In the second pane, you can view port scans and other attacks visually
and drill directly into them for further detail.�
The lower portion of the screen enables the security analyst to see the
types of things that are happening to the network in real time. Finally, the
lower, right hand portion of the screen provides a view by business unit, port
or any other NSM enabled field giving you a complete, holistic view of your
environment.
NSM Advanced Analytics Recommended System Requirements:
Operating System: Windows 2000 Server with SP2
Processor: Pentium4 2.0GHz
Memory: 1024MB RAM (128MB for OS plus 2M of RAM for every 1K events to be manipulated at one time)
Hard Drive: 7200 rpm IDE or 10K rpm SCSI
Display Adapter with 32MB+ RAM
Display Driver capable of 16M+ colors at 1280x1024
IPSEC Network Adapter: 3COM 3CR990-TX-97
Conclusion
NSM’s holistic approach, native intelligence, visual correlation and ability to seamlessly integrate analyst investigations enable any organization to understand the nature of security threats that occur both within and outside the enterprise. Its architecture is built with the enterprise in mind, ensuring that scalability, reliability and maintainability are achieved.
About
Intellitactics
Intellitactics provides a comprehensive solution for enterprise security management. Founded in 1996, its industry-leading Network Security Manager™ (NSM™) is the holistic, integrated threat management platform that enables security executives to police, prioritize and prevail across the full range of today's information security threats. NSM is the enterprise security management software of choice for many of the world's leading Global 1000 companies, government organizations and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) who seek to provide their organizations with comprehensive information security, leveraging the complete range of security information available from security devices and other information sources.
Visit the Authors Web Site
![]() �Click Here
for The Business Forum Library of
White Papers��
�Click Here
for The Business Forum Library of
White Papers��
![]()
�

 Search Our Site
Search Our Site
Search the ENTIRE Business
Forum site.�Search includes the Business
Forum Library, The Business Forum Journal and the Calendar Pages.
The Business ForumDisclaimer
The Business Forum, its Officers, partners, and all other
parties with which it deals, or is associated with, accept
absolutely no responsibility whatsoever, nor any liability,
for what is published on this web site.��� Please refer to:
Home��� Calendar��� The�Business�Forum�Journal���� Features��� Concept��� History
Library���� Formats��� Guest�Testimonials��� Client�Testimonials��� Experts��� Search
News�Wire���� Join��� Why�Sponsor���� Tell-A-Friend���� Contact The Business Forum
Beverly Hills, California United States of America
Email:� [email protected]
Graphics by DawsonDesign
Webmaster:�
bruceclay.com
�
� Copyright The Business Forum Institute 1982 - 2009� All rights reserved.
![]()